pylops.optimization.leastsquares.PreconditionedInversion¶
-
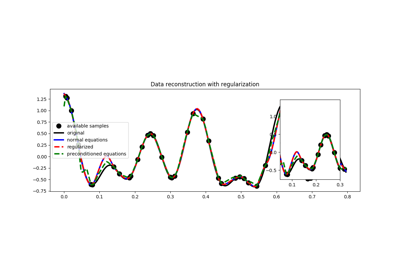
pylops.optimization.leastsquares.PreconditionedInversion(Op, P, data, x0=None, returninfo=False, **kwargs_lsqr)[source]¶ Preconditioned inversion.
Solve a system of preconditioned equations given the operator
Opand a preconditionerP.Parameters: - Op :
pylops.LinearOperator Operator to invert
- P :
pylops.LinearOperator Preconditioner
- data :
numpy.ndarray Data
- x0 :
numpy.ndarray Initial guess
- returninfo :
bool Return info of LSQR solver
- **kwargs_lsqr
Arbitrary keyword arguments for
scipy.sparse.linalg.lsqrsolver
Returns: - xinv :
numpy.ndarray Inverted model.
- xinv :
numpy.ndarray Inverted model \(\mathbf{Op}\)
- istop :
int Gives the reason for termination
1means \(\mathbf{x}\) is an approximate solution to \(\mathbf{d} = \mathbf{Op}\mathbf{x}\)2means \(\mathbf{x}\) approximately solves the least-squares problem- itn :
int Iteration number upon termination
- r1norm :
float \(||\mathbf{r}||_2\), where \(\mathbf{r} = \mathbf{d} - \mathbf{Op}\mathbf{x}\)
- r2norm :
float \(\sqrt{\mathbf{r}^T\mathbf{r} + \epsilon^2 \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x}}\). Equal to
r1normif \(\epsilon=0\)
See also
RegularizedInversion- Regularized inversion
NormalEquationsInversion- Normal equations inversion
Notes
Solve the following system of preconditioned equations given the operator \(\mathbf{Op}\), a preconditioner \(\mathbf{P}\), the data \(\mathbf{d}\)
\[\mathbf{d} = \mathbf{Op} (\mathbf{P} \mathbf{p})\]where \(\mathbf{p}\) is the solution in the preconditioned space and \(\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{P}\mathbf{p}\) is the solution in the original space.
- Op :