pylops.Sum¶
-
class
pylops.Sum(dims, dir, dtype='float64')[source]¶ Sum operator.
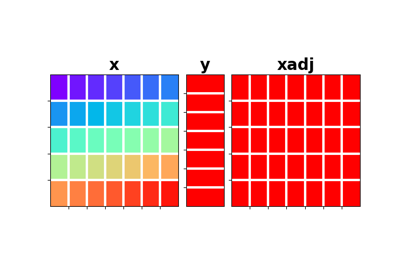
Sum along an axis of a multi-dimensional array (at least 2 dimensions are required) in forward model, and spread along the same axis in adjoint mode.
Parameters: Notes
Given a two dimensional array, the Sum operator re-arranges the input model into a multi-dimensional array of size
dimsand sums values along directiondir:\[y_j = \sum_i x_{i, j}\]In adjoint mode, the data is spread along the same direction:
\[x_{i, j} = y_j \quad \forall i=0, N-1\]Attributes: Methods
__init__(self, dims, dir[, dtype])Initialize this LinearOperator. adjoint(self)Hermitian adjoint. apply_columns(self, cols)Apply subset of columns of operator cond(self, \*\*kwargs_eig)Condition number of linear operator. conj(self)Complex conjugate operator div(self, y[, niter])Solve the linear problem \(\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}\). dot(self, x)Matrix-matrix or matrix-vector multiplication. eigs(self[, neigs, symmetric, niter])Most significant eigenvalues of linear operator. matmat(self, X)Matrix-matrix multiplication. matvec(self, x)Matrix-vector multiplication. rmatmat(self, X)Adjoint matrix-matrix multiplication. rmatvec(self, x)Adjoint matrix-vector multiplication. todense(self)Return dense matrix. transpose(self)Transpose this linear operator.