Note
Click here to download the full example code
1D Smoothing¶
This example shows how to use the pylops.Smoothing1D operator
to smooth an input signal along a given axis.
Derivative (or roughening) operators are generally used regularization in inverse problems. Smoothing has the opposite effect of roughening and it can be employed as preconditioning in inverse problems.
A smoothing operator is a simple compact filter on lenght \(n_{smooth}\) and each elements is equal to \(1/n_{smooth}\).
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylops
plt.close('all')
Define the input parameters: number of samples of input signal (N) and
lenght of the smoothing filter regression coefficients (\(n_{smooth}\)).
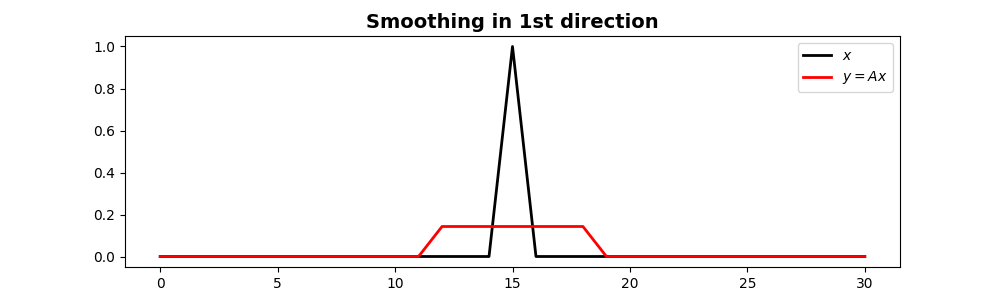
In this first case the input signal is one at the center and zero elsewhere.
N = 31
nsmooth = 7
x = np.zeros(N)
x[int(N/2)] = 1
Sop = pylops.Smoothing1D(nsmooth=nsmooth, dims=[N], dtype='float32')
y = Sop*x
xadj = Sop.H*y
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 3))
ax.plot(x, 'k', lw=2, label=r'$x$')
ax.plot(y, 'r', lw=2, label=r'$y=Ax$')
ax.set_title('Smoothing in 1st direction', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend()
Out:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f835c432048>
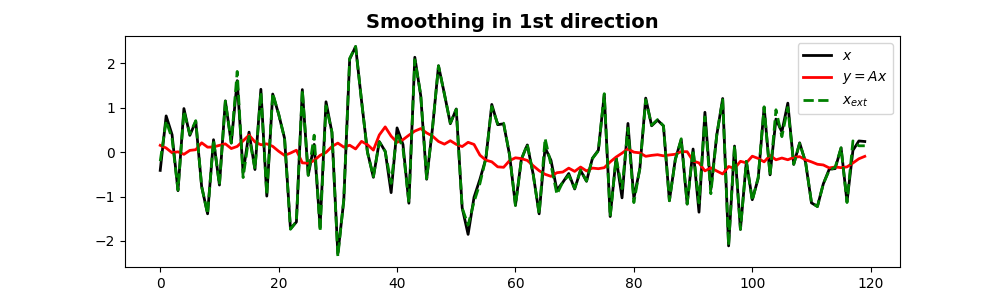
Let’s repeat the same exercise with a random signal as input. After applying smoothing, we will also try to invert it.
N = 120
nsmooth = 13
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, N)
Sop = pylops.Smoothing1D(nsmooth=13, dims=(N), dtype='float32')
y = Sop*x
xest = Sop/y
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 3))
ax.plot(x, 'k', lw=2, label=r'$x$')
ax.plot(y, 'r', lw=2, label=r'$y=Ax$')
ax.plot(xest, '--g', lw=2, label=r'$x_{ext}$')
ax.set_title('Smoothing in 1st direction',
fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend()
Out:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f8359e7a438>
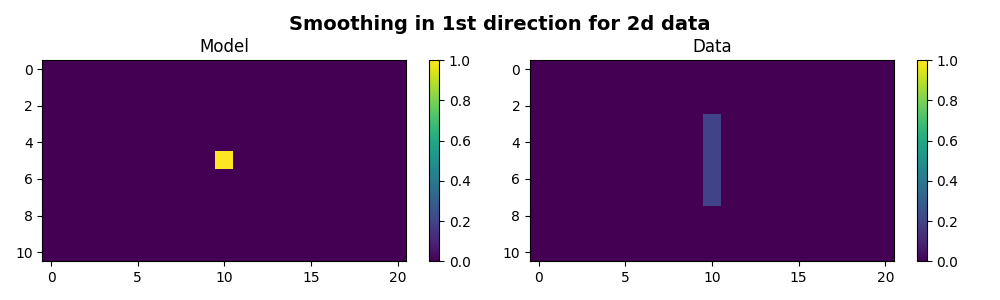
Finally we show that the same operator can be applied to multi-dimensional data along a chosen axis.
A = np.zeros((11, 21))
A[5, 10] = 1
Sop = pylops.Smoothing1D(nsmooth=5, dims=(11, 21), dir=0, dtype='float64')
B = np.reshape(Sop*np.ndarray.flatten(A), (11, 21))
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 3))
fig.suptitle('Smoothing in 1st direction for 2d data', fontsize=14,
fontweight='bold', y=0.95)
im = axs[0].imshow(A, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=1)
axs[0].axis('tight')
axs[0].set_title('Model')
plt.colorbar(im, ax=axs[0])
im = axs[1].imshow(B, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=1)
axs[1].axis('tight')
axs[1].set_title('Data')
plt.colorbar(im, ax=axs[1])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.8)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.924 seconds)