Note
Click here to download the full example code
Transpose¶
This example shows how to use the pylops.Transpose
operator. For arrays that are 2-dimensional in nature this operator
simply transposes rows and columns. For multi-dimensional arrays, this
operator can be used to permute dimensions
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pylops
plt.close("all")
np.random.seed(0)
Let’s start by creating a 2-dimensional array
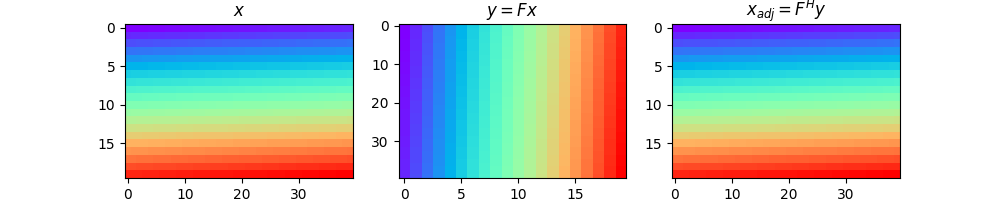
We use now the pylops.Transpose operator to swap the two
dimensions. As you will see the adjoint of this operator brings the data
back to its original model, or in other words the adjoint operator is equal
in this case to the inverse operator.
Top = pylops.Transpose(dims=dims, axes=(1, 0))
y = Top * x.ravel()
xadj = Top.H * y
y = y.reshape(Top.dimsd)
xadj = xadj.reshape(Top.dims)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 2))
fig.suptitle("Transpose for 2d data", fontsize=14, fontweight="bold", y=1.15)
axs[0].imshow(x, cmap="rainbow", vmin=0, vmax=800)
axs[0].set_title(r"$x$")
axs[0].axis("tight")
axs[1].imshow(y, cmap="rainbow", vmin=0, vmax=800)
axs[1].set_title(r"$y = F x$")
axs[1].axis("tight")
axs[2].imshow(xadj, cmap="rainbow", vmin=0, vmax=800)
axs[2].set_title(r"$x_{adj} = F^H y$")
axs[2].axis("tight")
Out:
(-0.5, 39.5, 19.5, -0.5)
A similar approach can of course be taken two swap multiple axes of multi-dimensional arrays for any number of dimensions.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.198 seconds)