pylops.signalprocessing.Shift#
- pylops.signalprocessing.Shift(dims, shift, axis=-1, nfft=None, sampling=1.0, real=False, engine='numpy', dtype='complex128', name='S', **kwargs_fftw)[source]#
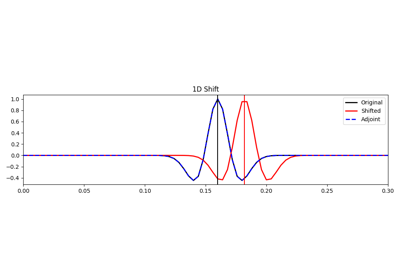
Shift operator
Apply fractional shift in the frequency domain along an
axisof a multi-dimensional array of sizedims.- Parameters
- dims
tuple Number of samples for each dimension
- shift
floatornumpy.ndarray Fractional shift to apply in the same unit as
sampling. For multi-dimensional inputs, this can be a scalar to apply to every trace along the chosen axis or an array of shifts to be applied to each trace.- axis
int, optional New in version 2.0.0.
Axis along which shift is applied
- nfft
int, optional Number of samples in Fourier Transform (same as input if
nfft=None)- sampling
float, optional Sampling step \(\Delta t\).
- real
bool, optional Model to which fft is applied has real numbers (
True) or not (False). Used to enforce that the output of adjoint of a real model is real.- engine
str, optional Engine used for fft computation (
numpy,scipy, orfftw). Choosenumpywhen working with CuPy arrays.- dtype
str, optional Type of elements in input array.
- name
str, optional New in version 2.0.0.
Name of operator (to be used by
pylops.utils.describe.describe)- **kwargs_fftw
Arbitrary keyword arguments for
pyfftw.FTTW
- dims
- Raises
- ValueError
If
dimsis provided andaxisis bigger thanlen(dims)- NotImplementedError
If
engineis neithernumpy,scipy, norfftw
Notes
The Shift operator applies the forward Fourier transform, an element-wise complex scaling, and inverse fourier transform
\[\mathbf{y}= \mathbf{F}^{-1} \mathbf{S} \mathbf{F} \mathbf{x}\]Here \(\mathbf{S}\) is a diagonal operator that scales the Fourier transformed input by \(e^{-j2\pi f t_S}\), where \(t_S\) is the chosen
shift.