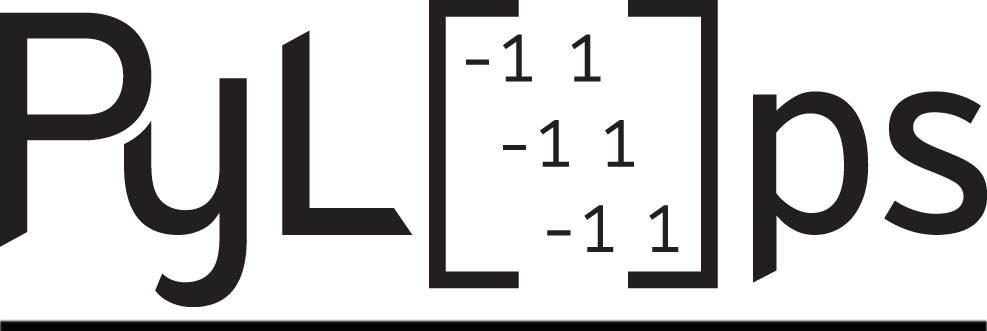pylops.CausalIntegration#
- class pylops.CausalIntegration(dims, axis=-1, sampling=1, kind='full', removefirst=False, dtype='float64', name='C')[source]#
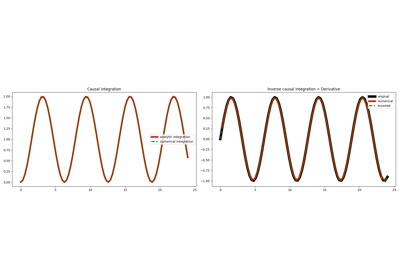
Causal integration.
Apply causal integration to a multi-dimensional array along
axis.- Parameters
- dims
listorint Number of samples for each dimension
- axis
int, optional New in version 2.0.0.
Axis along which the model is integrated.
- sampling
float, optional Sampling step
dx.- kind
str, optional Integration kind (
full,half, ortrapezoidal).- removefirst
bool, optional Remove first sample (
True) or not (False).- dtype
str, optional Type of elements in input array.
- name
str, optional New in version 2.0.0.
Name of operator (to be used by
pylops.utils.describe.describe)
- dims
Notes
The CausalIntegration operator applies a causal integration to any chosen direction of a multi-dimensional array.
For simplicity, given a one dimensional array, the causal integration is:
\[y(t) = \int\limits_{-\infty}^t x(\tau) \,\mathrm{d}\tau\]which can be discretised as :
\[y[i] = \sum_{j=0}^i x[j] \,\Delta t\]or
\[y[i] = \left(\sum_{j=0}^{i-1} x[j] + 0.5x[i]\right) \,\Delta t\]or
\[y[i] = \left(\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} x[j] + 0.5x[0] + 0.5x[i]\right) \,\Delta t\]where \(\Delta t\) is the
samplinginterval, and assuming the signal is zero before sample \(j=0\). In our implementation, the choice to add \(x[i]\) or \(0.5x[i]\) is made by selectingkind=fullorkind=half, respectively. The choice to add \(0.5x[i]\) and \(0.5x[0]\) instead of made by selecting thekind=trapezoidal.Note that the causal integral of a signal will depend, up to a constant, on causal start of the signal. For example if \(x(\tau) = t^2\) the resulting indefinite integration is:
\[y(t) = \int \tau^2 \,\mathrm{d}\tau = \frac{t^3}{3} + C\]However, if we apply a first derivative to \(y\) always obtain:
\[x(t) = \frac{\mathrm{d}y}{\mathrm{d}t} = t^2\]no matter the choice of \(C\).
- Attributes
Methods
__init__(dims[, axis, sampling, kind, ...])adjoint()apply_columns(cols)Apply subset of columns of operator
cond([uselobpcg])Condition number of linear operator.
conj()Complex conjugate operator
div(y[, niter, densesolver])Solve the linear problem \(\mathbf{y}=\mathbf{A}\mathbf{x}\).
dot(x)Matrix-matrix or matrix-vector multiplication.
eigs([neigs, symmetric, niter, uselobpcg])Most significant eigenvalues of linear operator.
matmat(X)Matrix-matrix multiplication.
matvec(x)Matrix-vector multiplication.
reset_count()Reset counters
rmatmat(X)Matrix-matrix multiplication.
rmatvec(x)Adjoint matrix-vector multiplication.
todense([backend])Return dense matrix.
toimag([forw, adj])Imag operator
toreal([forw, adj])Real operator
tosparse()Return sparse matrix.
trace([neval, method, backend])Trace of linear operator.
transpose()