pylops.utils.dottest#
- pylops.utils.dottest(Op, nr=None, nc=None, rtol=1e-06, atol=1e-21, complexflag=0, raiseerror=True, verb=False, backend='numpy')[source]#
Dot test.
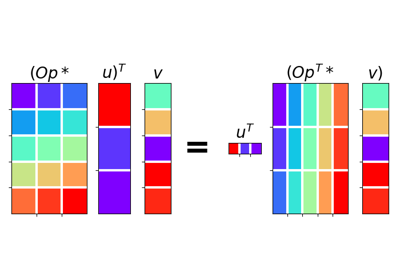
Generate random vectors \(\mathbf{u}\) and \(\mathbf{v}\) and perform dot-test to verify the validity of forward and adjoint operators. This test can help to detect errors in the operator implementation.
- Parameters
- Op
pylops.LinearOperator Linear operator to test.
- nr
int Number of rows of operator (i.e., elements in data)
- nc
int Number of columns of operator (i.e., elements in model)
- rtol
float, optional Relative dottest tolerance
- atol
float, optional Absolute dottest tolerance .. versionadded:: 2.0.0
- complexflag
bool, optional Generate random vectors with
0: Real entries for model and data1: Complex entries for model and real entries for data2: Real entries for model and complex entries for data3: Complex entries for model and data
- raiseerror
bool, optional Raise error or simply return
Falsewhen dottest fails- verb
bool, optional Verbosity
- backend
str, optional Backend used for dot test computations (
numpyorcupy). This parameter will be used to choose how to create the random vectors.
- Op
- Returns
- passed
bool Passed flag.
- passed
- Raises
- AssertionError
If dot-test is not verified within chosen tolerances.
Notes
A dot-test is mathematical tool used in the development of numerical linear operators.
More specifically, a correct implementation of forward and adjoint for a linear operator should verify the following equality within a numerical tolerance:
\[(\mathbf{Op}\,\mathbf{u})^H\mathbf{v} = \mathbf{u}^H(\mathbf{Op}^H\mathbf{v})\]