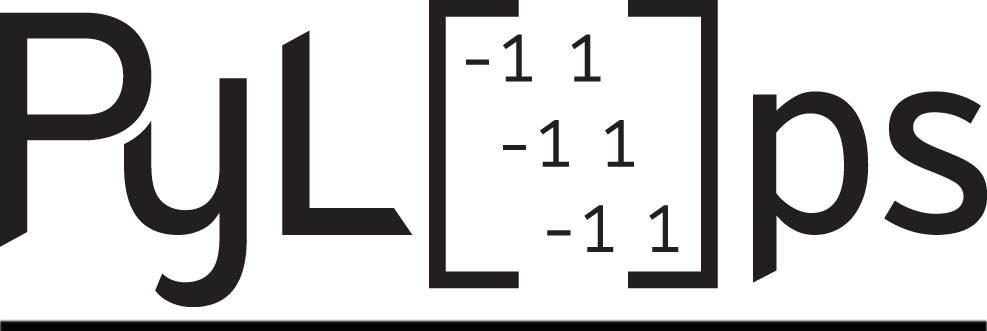pylops.waveeqprocessing.WavefieldDecomposition#
- pylops.waveeqprocessing.WavefieldDecomposition(p, vz, nt, nr, dt, dr, rho, vel, nffts=(None, None, None), critical=100.0, ntaper=10, scaling=1.0, kind='inverse', restriction=None, sptransf=None, solver=<function lsqr>, dottest=False, dtype='complex128', **kwargs_solver)[source]#
Up-down wavefield decomposition.
Apply seismic wavefield decomposition from multi-component (pressure and vertical particle velocity) data. This process is also generally referred to as data-based deghosting.
- Parameters
- p
np.ndarray Pressure data of size \(\lbrack n_{r_x} \,(\times n_{r_y}) \times n_t \rbrack\) (or \(\lbrack n_{r_{x,\text{sub}}} \,(\times n_{r_{y,\text{sub}}}) \times n_t \rbrack\) in case a
restrictionoperator is provided. Note that \(n_{r_{x,\text{sub}}}\) (and \(n_{r_{y,\text{sub}}}\)) must agree with the size of the output of this operator.)- vz
np.ndarray Vertical particle velocity data of same size as pressure data
- nt
int Number of samples along the time axis
- nr
intortuple Number of samples along the receiver axis (or axes)
- dt
float Sampling along the time axis
- dr
floatortuple Sampling along the receiver array (or axes)
- rho
float Density \(\rho\) along the receiver array (must be constant)
- vel
float Velocity \(c\) along the receiver array (must be constant)
- nffts
tuple, optional Number of samples along the wavenumber and frequency axes
- critical
float, optional Percentage of angles to retain in obliquity factor. For example, if
critical=100only angles below the critical angle \(\frac{f(k_x)}{c}\) will be retained- ntaper
float, optional Number of samples of taper applied to obliquity factor around critical angle
- kind
str, optional Type of separation:
inverse(default) oranalytical- scaling
float, optional Scaling to apply to the operator (see Notes of
pylops.waveeqprocessing.wavedecomposition.UpDownComposition2Dfor more details)- restriction
pylops.LinearOperator, optional Restriction operator
- sptransf
pylops.LinearOperator, optional Sparsifying operator
- solver
float, optional Function handle of solver to be used if
kind='inverse'- dottest
bool, optional Apply dot-test
- dtype
str, optional Type of elements in input array.
- **kwargs_solver
Arbitrary keyword arguments for chosen
solver
- p
- Returns
- pup
np.ndarray Up-going wavefield
- pdown
np.ndarray Down-going wavefield
- pup
- Raises
- KeyError
If
kindis neitheranalyticalnorinverse
Notes
Up- and down-going components of seismic data \(p^-(x, t)\) and \(p^+(x, t)\) can be estimated from multi-component data \(p(x, t)\) and \(v_z(x, t)\) by computing the following expression [1]:
\[\begin{split}\begin{bmatrix} \hat{p}^+ \\ \hat{p}^- \end{bmatrix}(k_x, \omega) = \frac{1}{2} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \frac{\omega \rho}{k_z} \\ 1 & - \frac{\omega \rho}{k_z} \\ \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} \hat{p} \\ \hat{v}_z \end{bmatrix}(k_x, \omega)\end{split}\]if
kind='analytical'or alternatively by solving the equation inptcpy.waveeqprocessing.UpDownComposition2Das an inverse problem, ifkind='inverse'.The latter approach has several advantages as data regularization can be included as part of the separation process allowing the input data to be aliased. This is obtained by solving the following problem:
\[\begin{split}\begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{p} \\ s\mathbf{v_z} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{R}\mathbf{F} & 0 \\ 0 & s\mathbf{R}\mathbf{F} \end{bmatrix} \mathbf{W} \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{F}^H \mathbf{S} & 0 \\ 0 & \mathbf{F}^H \mathbf{S} \end{bmatrix} \mathbf{p^{\pm}}\end{split}\]where \(\mathbf{R}\) is a
ptcpy.basicoperators.Restrictionoperator and \(\mathbf{S}\) is sparsyfing transform operator (e.g.,ptcpy.signalprocessing.Radon2D).- 1
Wapenaar, K. “Reciprocity properties of one-way propagators”, Geophysics, vol. 63, pp. 1795-1798. 1998.