Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Bilinear Interpolation#
This example shows how to use the pylops.signalprocessing.Bilinar
operator to perform bilinear interpolation to a 2-dimensional input vector.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy import misc
import pylops
plt.close("all")
np.random.seed(0)
First of all, we create a 2-dimensional input vector containing an image
from the scipy.misc family.
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/pylops/checkouts/latest/examples/plot_bilinear.py:19: DeprecationWarning: scipy.misc.face has been deprecated in SciPy v1.10.0; and will be completely removed in SciPy v1.12.0. Dataset methods have moved into the scipy.datasets module. Use scipy.datasets.face instead.
x = misc.face()[::5, ::5, 0]
We can now define a set of available samples in the first and second direction of the array and apply bilinear interpolation.
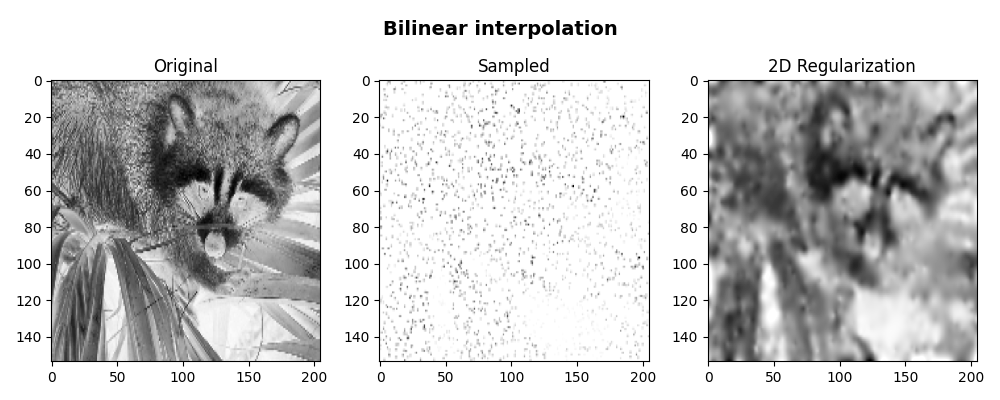
At this point we try to reconstruct the input signal imposing a smooth solution by means of a regularization term that minimizes the Laplacian of the solution.
D2op = pylops.Laplacian((nz, nx), weights=(1, 1), dtype="float64")
xadj = Bop.H * y
xinv = pylops.optimization.leastsquares.normal_equations_inversion(
Bop, y, [D2op], epsRs=[np.sqrt(0.1)], **dict(maxiter=100)
)[0]
xadj = xadj.reshape(nz, nx)
xinv = xinv.reshape(nz, nx)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 4))
fig.suptitle("Bilinear interpolation", fontsize=14, fontweight="bold", y=0.95)
axs[0].imshow(x, cmap="gray_r", vmin=0, vmax=250)
axs[0].axis("tight")
axs[0].set_title("Original")
axs[1].imshow(xadj, cmap="gray_r", vmin=0, vmax=250)
axs[1].axis("tight")
axs[1].set_title("Sampled")
axs[2].imshow(xinv, cmap="gray_r", vmin=0, vmax=250)
axs[2].axis("tight")
axs[2].set_title("2D Regularization")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.8)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.979 seconds)